1. Objective Overview (What & Why)
The goal is to enhance TKLLM with TikTok-style content virality intelligence. Instead of only generating stylistically consistent scripts, TKLLM becomes an algorithm-aware content generator capable of producing content with high virality potential.
Detailed objectives:
-
Data Filtering Layer (High-Value Sample Selection)
-
Use ViralScore to identify historical posts with the highest propagation potential.
- Assign higher training weight to these posts.
-
Reduces noise in the training set and emphasizes patterns correlated with virality.
-
Training Objective Layer (Virality as Signal)
-
Integrate virality signals as an auxiliary loss or reward function.
- Encourages the model to internalize features that drive shares, comments, replays, and watch-through rates.
-
Supports both multi-task learning and optional reinforcement learning approaches.
-
Generation-Time Optimization (Decoding & Reranking)
-
Apply ViralScore at decoding: rerank candidate outputs, bias sampling probability, or constrain decoding toward high-virality styles.
-
Achieves virality improvements without full retraining.
-
Evaluation & Feedback Loop
-
Build offline metrics (predicted vs actual virality) and online A/B tests.
- Close the loop by feeding real engagement back to the model for continual improvement.
Key Principle: ViralScore augments TKLLM without compromising language quality or controllability.
2. System Architecture (High-Level)
[Raw TikTok Data / Creators] -> Data Lake -> Feature Extraction -> ViralScore Estimator
↘ ↘
↘ High-Value Sample Selector
↘ ↘
Style Embedding DB --------> TKLLM Training Pipeline (GSPF)
↘
↘
Generation API -> Reranker (Viral Reward)
↘
Publish / A-B Test -> Online Feedback -> Metrics DB
Component Details:
-
Raw TikTok Data / Creators
-
Historical videos, titles, captions, hashtags, engagement metrics, audio/visual content.
-
Data Lake
-
Centralized repository storing raw multimodal data for large-scale batch processing.
-
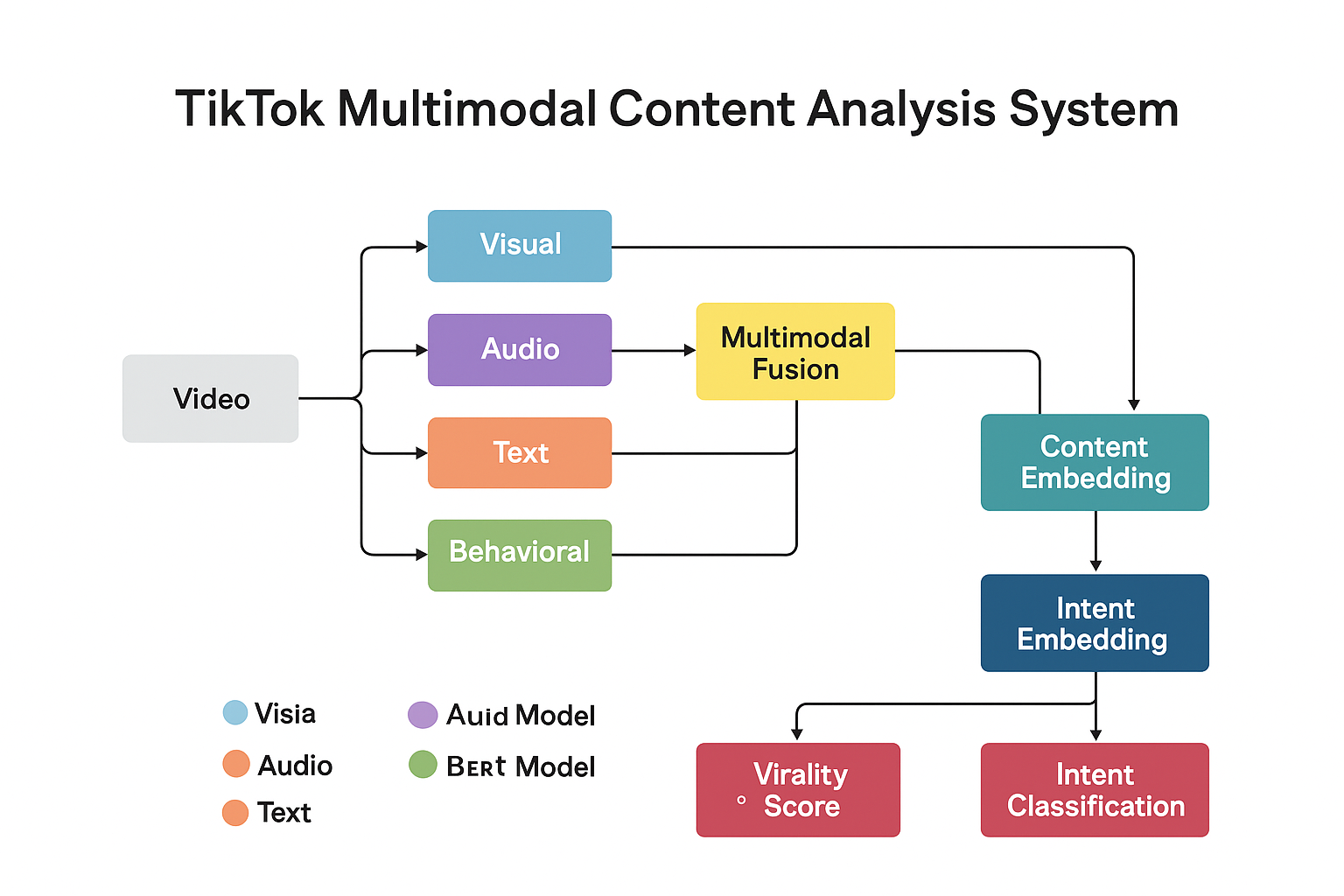
Feature Extraction
-
Text: BERT/GPT embeddings, token counts, sentiment scores.
- Visual: CLIP/ViT embeddings of key frames.
- Audio: MFCC features, rhythm, emotional spectrum.
-
Temporal/behavioral: CTR, watch-through, replays, early view trajectories.
-
ViralScore Estimator
-
Predicts potential virality for a given post.
-
Multimodal Transformer-based encoder, outputs scalar ViralScore and subcomponent breakdowns (E, H, R, S, T).
-
High-Value Sample Selector
-
Applies thresholds or weighted sampling based on ViralScore.
-
Outputs priority training set.
-
Style Embedding DB
-
Stores latent style embeddings for creator-specific replication.
-
TKLLM Training Pipeline (GSPF)
-
Gradient Surgical Fine-tuning with sample weighting or auxiliary viral loss.
-
Supports incremental updates using online feedback.
-
Generation API
-
Produces N candidate scripts for a given prompt.
-
Viral Reward Reranker
-
Re-ranks candidates according to ViralScore.
-
Optionally applies reward-augmented decoding.
-
Online Feedback & Metrics DB
- Collects real-world engagement data to continuously refine ViralScore and LM.
3. Viral Model Design (Core Algorithm)
3.1 ViralScore Components
| Component | Description | Feature Examples |
|---|---|---|
| EmotionIntensity (E) | Captures emotional arcs across content | Sentiment flow, arousal curves, facial expression embeddings |
| HookStrength (H) | Measures appeal in first 3 seconds | Thumbnail attractiveness, first sentence CTA, music hook |
| Replicability (R) | Likelihood content is imitable or templateable | Memetic formats, challenge potential, repeatable captions |
| ShareTrigger (S) | Mechanisms prompting user engagement | Surprise elements, controversy, educational “aha” moments |
| TrendMatch (T) | Alignment with trending topics/culture | Hashtags, trending audio, regional trends |
Score Calculation:
\[ V = \sigma(\alpha E + \beta H + \gamma R + \delta S + \epsilon T) \]
- \(\sigma\) = squashing function (sigmoid, scaled softmax)
- Coefficients \(\alpha\ ... \epsilon\) = learned via regression or tuned heuristically
3.2 Model Inputs (Multimodal)
-
Textual Features
-
Titles, captions, comments embeddings
-
Topic vectors, sentiment, word counts
-
Visual Features
-
First/ key frame embeddings via CLIP/ViT
-
Motion / scene complexity metrics
-
Audio Features
-
Rhythm, pitch variance, energy levels
-
Music genre embeddings
-
Behavioral Signals
-
Early CTR, watch-through rate, shares, replays
-
Temporal/Trend Features
-
Posting hour, weekday, hashtag trend strength, geographic info
3.3 Architecture Recommendations
-
Multimodal Encoder
-
Independent encoders per modality
-
Cross-attention fusion layer to capture multimodal interactions
-
Temporal Module (Optional)
-
1D CNN or Temporal Transformer to capture emotion or engagement dynamics over time
-
MLP Head
-
Predicts ViralScore scalar and optionally subcomponent scores (E, H, R, S, T)
-
Training Objectives
-
Supervised regression on real propagation metrics
- Optional rank-based loss for pairwise ranking of content
- Multi-task auxiliary loss for subcomponents
4. Training Data & Labels
4.1 Label Sources
-
Real Behavior Signals (High Quality)
-
24h / 72h post-release plays, shares, comments
-
Watch-through rate and rewatch frequency
-
Platform Proxy Signals (Weak Supervision)
-
Early small-batch CTR, early replays, early engagement metrics
-
Human Labels (Optional for Cold Start)
-
Experts annotate hook strength, replicability, trend alignment
4.2 Sample Construction
- Positive samples: top X% viral content
- Negative samples: low engagement or failed content
- Balanced stratification by content type: drama, education, e-commerce, dance
4.3 Data Augmentation
- Text perturbation: replace CTAs, rephrase hooks
- Temporal sampling: early engagement sequences, multiple time windows
- Synthetic “mirrored” challenges: minor variant content to improve replicability detection
5. Integrating ViralScore into TKLLM Training
Entry Point A — Sample Weighting
\[ \mathcal{L} = \frac{1}{N} \sum_i w_i \cdot \mathcal{L}_{CE}(y_i, \hat{y}_i), \quad w_i = 1 + \lambda V_i \]
- Biases LM towards high-virality patterns
- Easy to implement with GSPF
Entry Point B — Auxiliary Loss
\[ \mathcal{L} = \mathcal{L}*{LM} + \mu \cdot \mathcal{L}*{Viral}, \quad \mathcal{L}_{Viral} = \text{MSE}(V, \hat{V}) \]
- Internal representation learns virality-aware semantics
- Multi-task learning improves transfer to unseen content
Entry Point C — Generation-Time Reward / Reranking
- Reranking: generate N candidates → compute ViralScore → select top
- Reward-Augmented Decoding:
\[ \text{score}(c) = \log P_{LM}(c) + \eta \cdot \text{ViralScore}(c) \]
- RL Fine-Tuning (optional, cautious): PPO/TRPO using ViralScore as reward
- Benefits: improves output without full retraining, flexible deployment
6. Training Implementation (Pseudocode)
6.1 ViralScore Training
model = MultiModalViralModel()
optimizer = Adam(model.parameters(), lr=1e-4)
for epoch in range(EPOCHS):
for batch in loader:
features, labels = batch
preds = model(features)
loss = mse(preds, labels)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
optimizer.zero_grad()
6.2 GSPF Fine-Tuning with Weighted Samples
for epoch in range(EPOCHS):
for batch in data_loader:
inputs, targets, viral_scores = batch
outputs = model(inputs)
lm_loss = cross_entropy(outputs, targets, reduction='none') # per-token
sample_loss = lm_loss.mean(dim=1)
weights = 1.0 + lambda_v * viral_scores
weighted_loss = (weights * sample_loss).mean()
weighted_loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
optimizer.zero_grad()
6.3 Generation & Rerank
def generate_with_rerank(prompt, model, viral_estimator, k=16):
cands = model.sample(prompt, num_samples=k, temperature=0.9)
scored = []
for cand in cands:
features = extract_features(cand)
vscore = viral_estimator.predict(features)
score = logprob(model, cand) + eta * vscore
scored.append((score, cand, vscore))
best = max(scored, key=lambda x: x[0])
return best[1], best[2]
7. Evaluation & A/B Testing
Offline Metrics
- ViralScore MSE / Spearman: prediction accuracy of propagation
- Perplexity / BLEU / ROUGE: language quality
- LM+Viral combined ranking: human evaluation for viral appeal
Online Metrics (A/B Test)
- A (baseline): vanilla TKLLM outputs
- B (Viral-augmented): sample-weighted + rerank
KPIs:
- Day-1 play growth (Δ plays)
- Watch-through rate
- Share/forward rate
- Rewatch rate
- Conversion rate (click/purchase)
Statistical significance: bootstrap / t-test.
8. Deployment & Inference Optimization
- Deploy Viral Estimator as REST/GRPC microservice
- Model compression: quantization (8/4-bit) or distillation
- Batch evaluation: generate N candidates → batch scoring → rerank
- Latency control: two-stage lightweight+heavy scoring; rerank <500ms for 15s scripts
9. Online Feedback & Learning Loop
- Data Collection: 1h/24h engagement metrics
- Sample Pool Refresh: automated high-virality sample inclusion
- Incremental Training: GSPF dynamic freezing for low-cost updates
- Iteration Cycle: stabilize metrics → expand A/B → full rollout
10. Safety, Ethics & Abuse Prevention
- Abuse Prevention: avoid incentivizing controversy or misinformation
- BrandSafety / PolicyPenalty: sensitive content reduces ViralScore or is blocked
- Controlled RL: constrained decoding, topic/word blacklists
- Transparency: subscore breakdown (E,H,R,S,T) for auditing